One of the important presumption for daylight evaluation in buildings is to identify external daylight sources. These are the direct sunlight and diffuse light of the sky. Up to now, several computational models for simulation of the sky light were developed. These models describe overcast sky situation, sunny situation and statistically found out samples of the sky.
CIE Overcast Sky - 1942
CIE model of uniform overcast sky represents daylight conditions at a uniform cloudiness with luminance gradation 1: 3 from horizon to zenith. The influence of direct sunlight is excluded. The model is the basis of lighting engineering standards for the design and evaluation of daylight in building interiors.

▼Moon, P., Spencer, D.E. Illumination from a nonuniform sky. Illuminating Engineering, 1942, 37, 10, p.707-726.
▼CIE 16:1970. Daylight. Technical Report. Vienna: CIE Central Bureau, 1970.
CIE Clear Sky - 1973
Cie model of clear sky enables modelling of the sky luminance distribution on the clear sky without clouds. This model was adopted by CIE for daylight calculations and evaluations of shading devices during sunny situations.
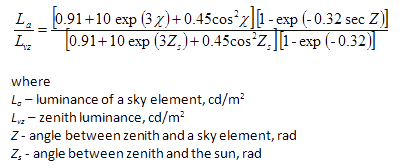
▼Kittler, R. Standardisation of outdoor conditions for the calculation of the Daylight Factor with clear skies. Proc. Conf. Sunlight in Buildings. Rotterdam: Bouwcentrum, 1967, p. 273-286.
(Kittler_Bouwcentrum_1967.pdf)
▼CIE 22:1973. Standardisation of luminance distribution on clear skies. Technical Report, Paris: CIE Central Bureau, 1973.