▼ Navvab M. Scale model photometry techniques under simulated sky conditions. Journ. of IES, 1996, 25(2): 160-172. (Mojtaba_96- IESNAmoji1996ScaleModelPhotometry.pdf)
Ann Arbor artificial sky, USA
Bartenbach GmbH. artificial sky, Aldrans, Austria
▼Künstlicher Himmel (Artificial sky, in Austria), Bartenbach GmbH, https://www.bartenbach.com/en/lighting-design/the-artificial-sky.html
The Bartlet Lighting Simulator, University College London, U.K.
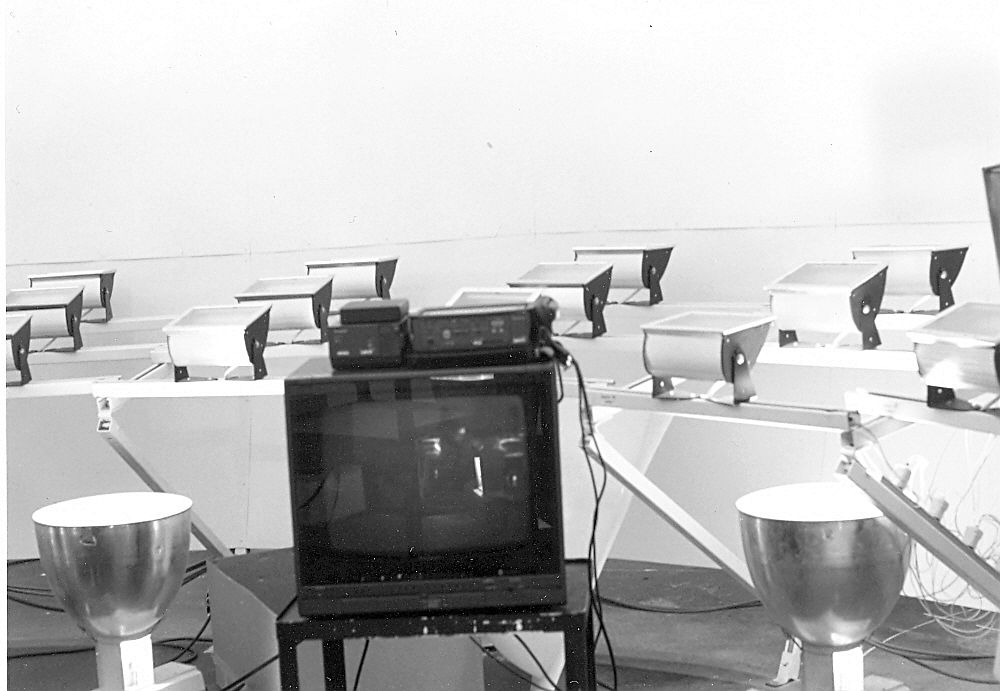
Artificial sky at Institute of Construction and Architecture in SAS, Bratislava, Slovakia
Artificial sky in the Institute of Construction and Architecture, 1973 – 2015
▼ Kittler R. A new artificial ’Overcast and Clear Sky’ with artificial sun for daylight research. Lighting Research and Technology, 6, 1974, 4, 227-229
(KITTLER_LRT_1974-4-227_New-artificial ‘overcast and clear’ sky with_artificial sun.pdf)
▼Iliť Š. Experimentálny výskum svetlotechnických vlastností stavebných prvkov a systémov. Umelá obloha pre svetelnotechnický experimentálny výskum. (Experimental research of illuminating engineering properties of building elements and systems. The artificial sky for illuminating engineering experimental research. Final Report, Part I a). P 12-121-001-002-03/3 Záver. správa, časť I a, Bratislava: ÚSTARCH SAV, 84 p., 1973. In Slovak
(expIlit. experimentalny vyskum svetlotech.vlastnosti….pdf)
▼Ondrejička Š. Experimentálny výskum svetlotechnických vlastností stavebných prvkov a systémov. I b. Svetelné polia a riadenie svietivosti zdrojov pri ich vytváraní v umelej oblohe. (Experimental research of illuminating engineering properties of building elements and systems. Light fields and control of source luminous intensities for consruction in the artificial sky. Final Report, Part I b). P 12-121-001-002-03/3 Záver. správa, časť I b, Bratislava: ÚSTARCH SAV, 117 p., 1973. In Slovak
▼Kittler, R. Experimentálny výskum svetlotechnických vlastností stavebných prvkov a systémov. Modelovanie prírodných svetelných polí v umelej oblohe. (Experimental research of illuminating engineering properties of building elements and systems. Modelling of natural light fields in an artificial sky. Final Report, Part I c). P 12-121-001-002-03/3 Záver. správa, časť I c, Bratislava: ÚSTARCH SAV, 164 p., 1973. In Slovak
▼Darula, S. Artificial sky: Possibilities to evaluate daylight in models. Proc. Int. Conf. Indoor Climate of Buildings ´98. Health and Comfort vs. Intelligent Technology, Štrbské Pleso 1 – 3. 12. 1998. SSTP Bratislava, 1998, p. 79-82.
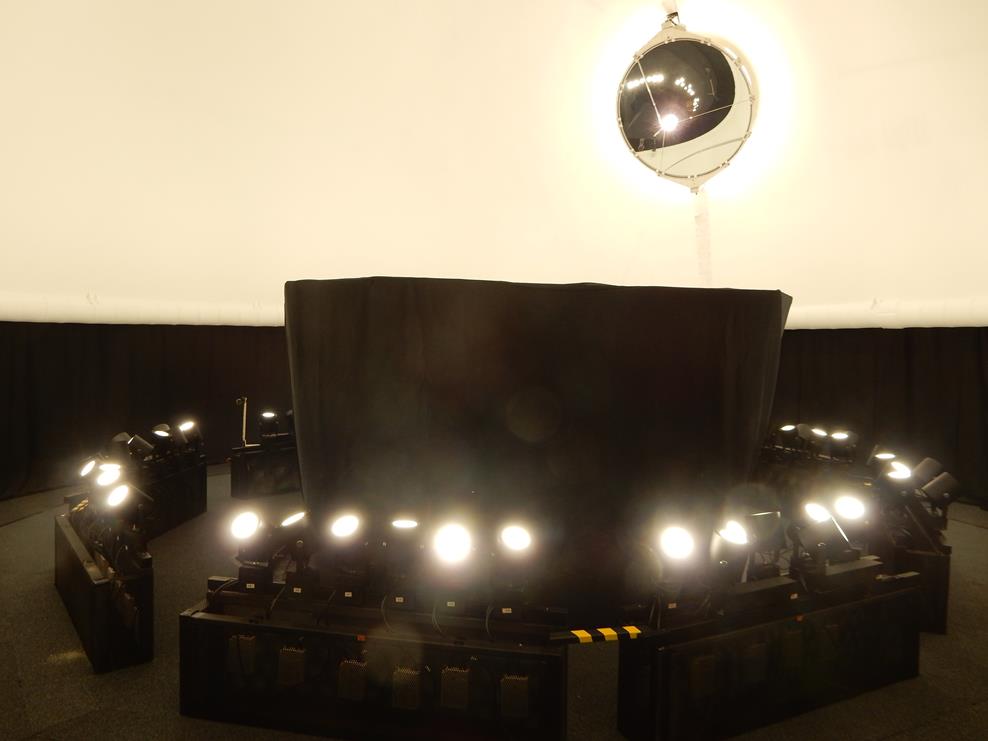
Artificial sky in the Institute of Construction and Architecture - new generation, 2015 - present
▼Darula, S. Relation between direct and diffuse daylight illuminance. LUMEN V4 : proceedings of international conference 8-10 Október 2014, Visegrád, Hungary [elektronický zdroj]. Editor Zoltán Toth. – Budapest : MEE Világítástechnikai Társaság, 2014, 6 p.
(Darula_2014_Lumen_V4_Relation between direct and diffuse.pdf)
▼Darula, S. – Kittler R. A methodology for designing and calibrating an artificial sky to simulate ISO/CIE sky types with an artificial sun. Leukos, 2015, vol. 11, no. 2, p. 93-105.
(Darula_Kit_LEUKOS_15_A methodology for Designing and Calibrating.pdf)
▼Kittler, R. – Darula, S. The Natural Redistribution of Sunlight and Skylight Due to the Atmospheric Turbidity of Cloudless Skies. Leukos, 2018, vol. 14, no. 2, p. 87-93.
▼Darula, S. – Kittler R. Deriving illuminance for model measurements under artificial skies. Proceedings of 28th CIE Session 2015 : CIE 216:2015.Volume 1 Part 2. – Vienna : CIE Central Bureau, 2015, p. 1148-1158.
(Darula_2015_CIE Session_Deriving illuminance.pdf)
▼Kittler R. – Darula, S. The simultaneous occurrence and relationship of sunlight and skylight under ISO/CIE standard sky types. Lighting Research and Technology, 2015, vol. 47, p. 565-580.
(Kittler-Dar_LRT–2015-565-80_The simultaneous occurrence .pdf)
▼Kittler R. – Darula, S. The research search for the least beneficial overcast sky and progress in defining its luminance gradation. Building Research Journal, 2014, vol. 61, no. 3, p. 151-166.
(KIttler_Darula_brj-2014-0012-The research search___Reprint.pdf)
▼Kittler R. – Darula, S. The experience with the design and refurbishment of the artificial sky in the SAS daylight laboratory. LIGHT SVĚTLO 2015: proceedings of the 21st international conference. Brno : Brno University of Technology, 2015, p. 205-208.
(Kittler_2015_konf-Svetlo_The experience.pdf)
▼Darula, S. – Kittler R. Parameterisation of direct illuminance for an artificial sky with sun. LUMEN V4: proceedings VI. IEEE lighting conference of the Visegrad countries. – 2016, p. 213-216.
(Darula_2016_Lumen_V4_Parameterisation of direct.pdf)
▼Kittler R. – Darula, S. Scattered sunlight determining sky luminance patterns. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, vol. 62, p. 575-584.
(Kittler_Dar_2016_RSER_reprint.pdf)
▼Maňková, L. – Hartman, P. – Habuliak, P. – Darula, S. The Inffuence of photometric coating on spectral reflectance of artificial sky dome. LUMEN V4: proceedings VI. IEEE lighting conference of the Visegrad countries. – 2016, p. 250-253.
(Mankova_Han_Dar_2016_IEEE_Lumen_The Influence of Photometric Coating__07745556.pdf)
▼Darula,S., Kittler, R., Malíkova,M..2017. Modelling of Daylight Sources in the Artificial Sky. Applied Mechanics and Materials,861, p. 469-476.
(Darula_KIT_Mal_2017_AMM_Modelling_.861.469.pdf)
▼Darula, S. – Kittler, R. The new generation of an artificial sky: simulating various overcast sky conditions. In Lux Europa 2017: Proceedings of the European lighting conference, September 18-20, 2017, Ljubljana. Ljubljana: Lighting Engineering Society of Slovenia, 2017, p. 401-405.
(Darula_KIT_LuxEuropa2017_Artificial calibration overcast.pdf)
▼Kittler, R. – Darula, S. The Natural Redistribution of Sunlight and Skylight Due to the Atmospheric Turbidity of Cloudless Skies. Leukos, 2018, vol. 14, no. 2, p. 87-93.
(Kittler_2018_Leukos_The Natural Redistribution of Sunlight and Skylight.pdf)
Welsh School of Architecture,Cardiff University, U.K.
▼ Mansy, K., O’Hara, S., Gedra, T., Arsalan, Q. Electronically-Controlled Artificial Sky Dome @ OSU. … in Progress. Proceedings of the 2005 American Society for Engineering Education Annual Conference & Exposition, American Society for Engineering Education, pp. 5123-5131.
ftp://ftp.ni.com/pub/gdc/tut/electrocon..pdf (CARDIFF_electrocon..pdf)
▼ Daylight modelling: the sky dome. Cardiff University.
http://www.cgarchitect.com/content/posts/features/2012_09/barcelona_harbor/skydome-modelling.pdf
Artificial sky in Stuttgart, Germany
▼ Kesten, D., Fiedler, S., Thumm, F., Löffler, A. and Eicker, U. Evaluation of daylight performance in scale models and a full-scale mock-up office. International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies 2010, 5, 158–165.
NIISF artificial sky, Moscow, Russia
▼Lioutsko KV, Spiridonov AV. 1992 Artificial sky for use with large-scale architectural daylight models. Lighting Res. Technol. 24(1): 25-28.
(LIOUTSKO_LRT_1992-1-25_Artificial sky for _large-scale architectural.pdf)
Cambridge, U.K.
▼ Croghan, D. Daylighting buildings. Technical papers 1964/70, Cambridge, 2015.
(Croghan D, ‘Daylighting Buildings’ (technical papers 1964-1970).pdf)
LBL, USA
▼ Navvab M. 1981. Development and use of a hemispherical sky simulator. LBL Report 13400.
Sekisui House, Japan
▼ Nakamura, H., Okado, M., Kawasaki, Y., Koga, Y. A New artificial sky in Japan.
(Nakamura_Okado_A new artificial sky -system_1991_rukopis_FK2618.pdf)